|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| pics | ||
| samples | ||
| typetapper | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| README.md | ||
| install.sh | ||
| plugin.toml | ||
README.md
TypeTapper
Audrey Dutcher CSE 578 Fall 2022
TypeTapper is a tool to visualize structure usage patterns in binaries.
Installation
To install, run the installation script: ./install.sh.
It is highly recommended you do this in a virtualenv!
This will install dependencies, and then link TypeTapper into the plugin loading path for angr-management.
Booting
Start angr-management: python -m angrmanagement.
Click in the toolbar: Plugins -> Manage Plugins... and check the box next to TypeTapper, then press Ok.
Load a binary to analyze from the File menu. Several good samples are provided in the samples directory.
As an example, let's use the corewars-vm binary.
Click through the loading and analysis options screens, using the default settings.
Wait for autoanalysis to finish.
Click on the code that appears and press the Tab key to decompile it.
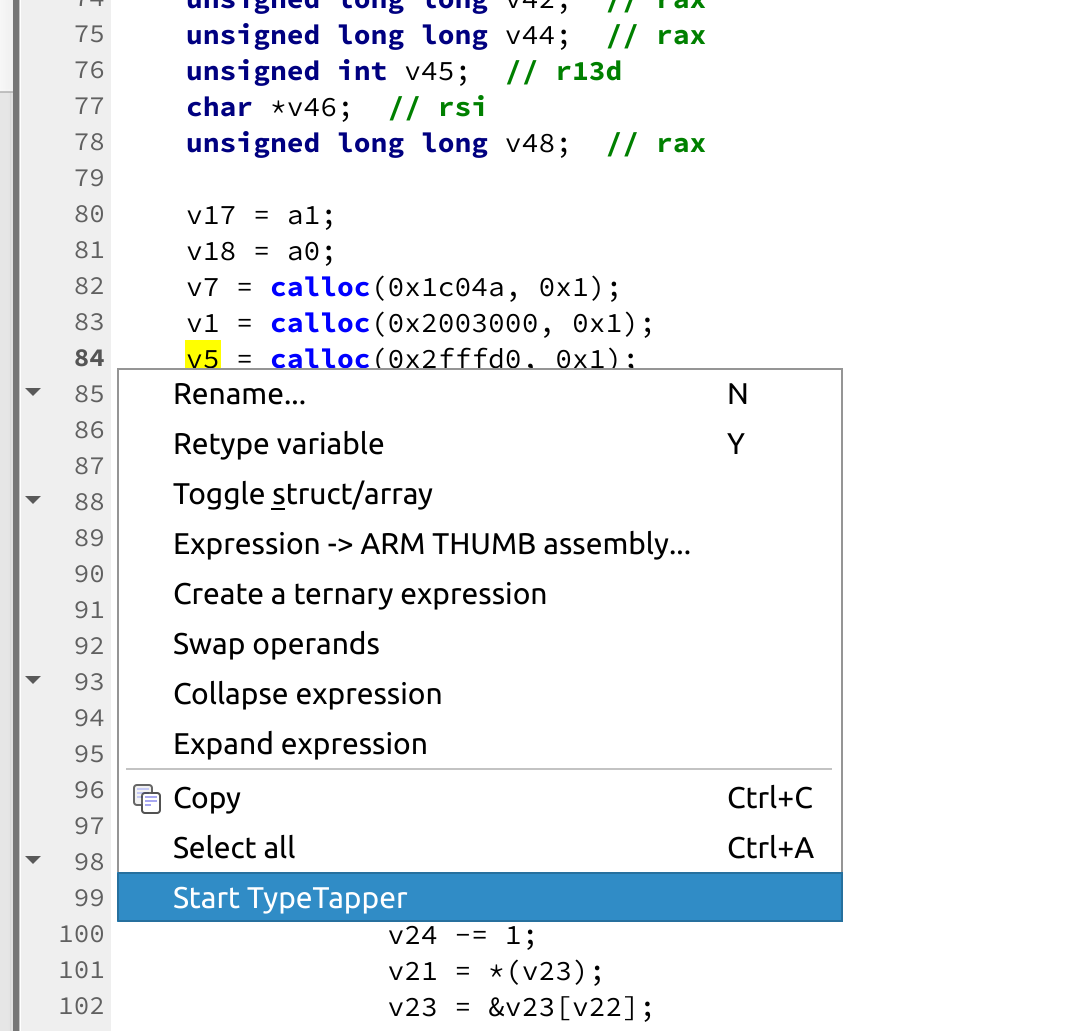
Finally, right-click on a variable usage you're interested in and select "Start TypeTapper".
In corewars-vm, a good variable to use is any of the variables assigned from a call to calloc.
Usage
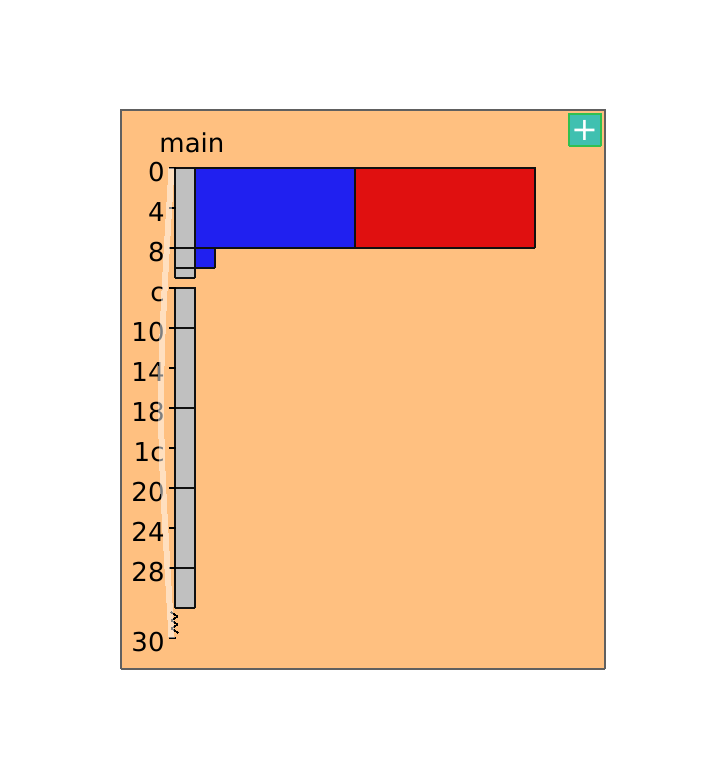
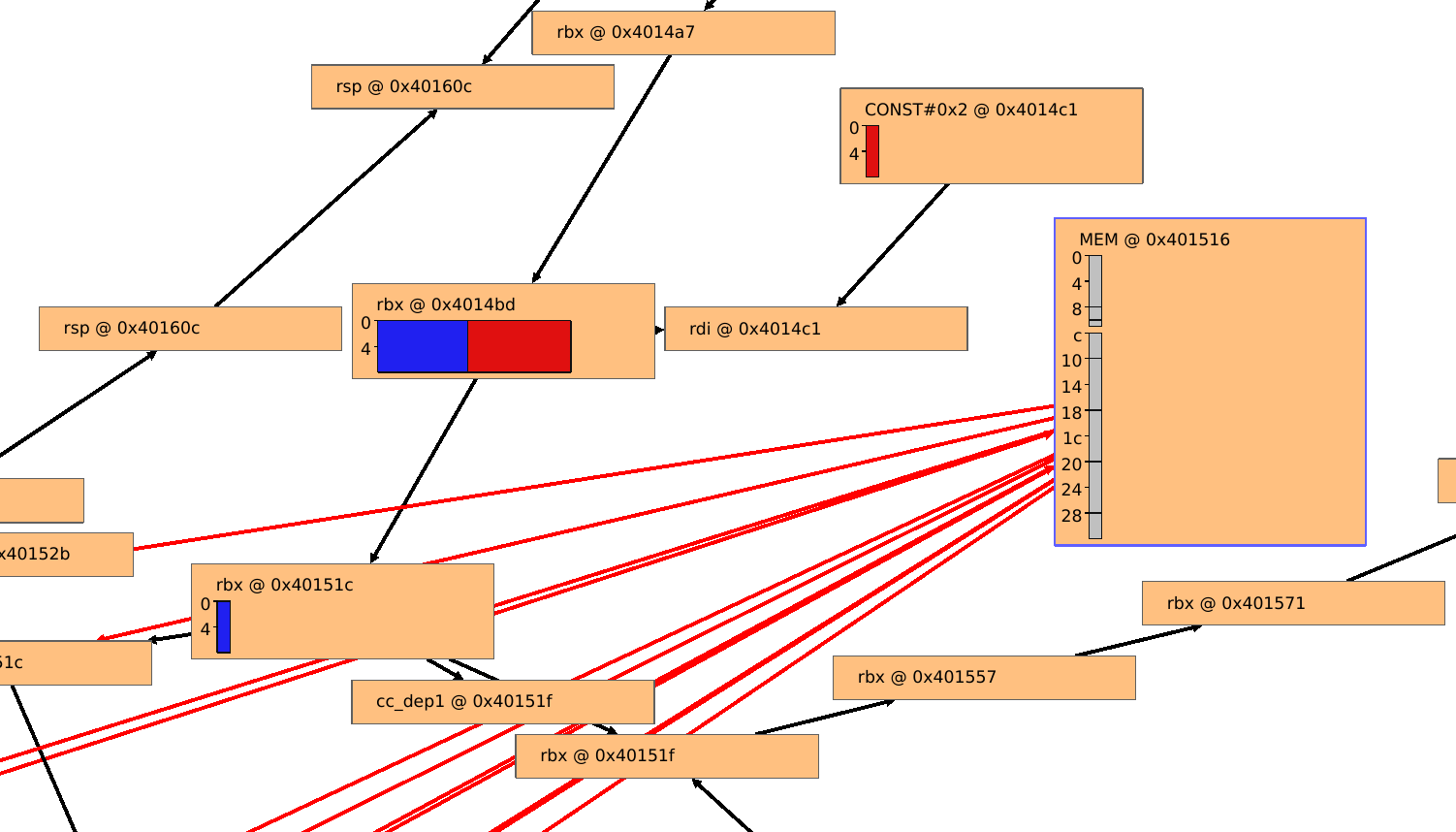
The main view of TypeTapper is an interactive node-link diagram, initially populated by one node.
Interactions
- To populate it with more nodes, click on the blue plus icon and then click on one of the nodes which appears to commit it to the graph.
- Click and drag a node to reposition it.
- Hold down the Z key to run the graph layout algorithm on the current layout.
- Double-click on a node to enter a new view with that node's children in it. If you double-click on a node which has no children, you will be navigated to the corresponding point in the disassembly.
- Double-click on the background to undo this operation and navigate to the parent view. To undo navigating to the disassembly, click on the tab in the tab bar labeled "TypeTapper".
- Click and drag on the background to pan the view.
- Hold Shift, then click and drag on the background to select multiple nodes.
- Right-click on a selected node or nodes to view context actions, including creation and restructuring of node groupings.
- Drag a node into another node to move the dragged node into the target node's group.
- Hold down the X key to enter rapid-fire expand mode, where hovering nodes with the mouse will immediately commit and expand them.
Code structure
data.pyis the record structures used by the analysis and the visualization, as well as some very primitive algorithms for manipulating them.engine.pyis the emulator logic for the static analysis. It describes how to interpret Valgrind's VEX IR as directives for producing the data domain we're working with.analysis.pyis the coordinator logic for the static analysis. It runs in two phases, first applying the engine to each basic block of the program, and then stitching the results together with the help of a control flow graph.knowledge.pyis the angr knowledge base plugin to store the static analysis result.procedures.pyis a collection of function summaries to provide meaningful results when analyzing imported library functions without having to look at their code.relative_graph.pyis the first-level data structure used during the visualization. It generates and stores a view of the graph from the static analysis results such that each node in the derived view contains properties relative to a starting node.hierarchy_graph.pyis the second-level data structure used during the visualization. It organizes nodes from the relative graph into a hierarchy, storing data in such a way that it is efficient to query relationships between nodes at different levels of hierarchy.plugin.pyis the angr-management plugin definition. It handles the UI elements outside the main TypeTapper view as well as coordinating the initial analysis.hierarchy_graph_view.pyis the visualization UI code. It defines the main TypeTapper widget, its rendering and interactions, the subcomponent graphical items, and their behaviors.